The most important part of lymphoma treatment is determining whether the disease is refractory or stable. The oncologist will determine the type of treatment and discuss the pros and cons. They will also make recommendations based on published guidelines. The types of treatments for lymphoma include a variety of drugs, chemotherapy, and surgery. In addition to the medical treatment, patients must also decide whether to continue with their normal lives.
The first step in treating lymphoma is to determine its exact etiology. Although no single cause of lymphoma has been found, lymphocytes can be cancerous even if they are healthy. A proper diagnosis can help determine which type of treatment is most appropriate. The next step is to determine the severity of the disease. Then, the patient will receive a treatment plan. This may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or biologic therapy.
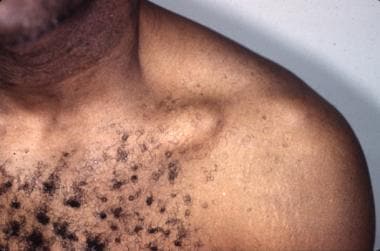
There are more than 70 different types of lymphoma, and the symptoms and treatments are based on the specific type of lymphoma. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available. The right diagnosis can help determine which treatment is most suitable for you. Your doctor will assess your health and preferences to come up with a treatment plan that meets your needs. Then, your treatment plan will be based on your condition and preferences.
The second step in lymphoma treatment is to consider a patient’s age. In Australia, people with lymphoma can be diagnosed at any age and at any stage of life. Luckily, most patients survive for years following diagnosis. However, if you are diagnosed with lymphoma early, it is important to understand that treatment options for this disease are not as common as they might be in other countries.
The best way to learn about lymphoma is to seek professional help. There are dozens of treatment options. In some cases, the most common treatments are chemotherapy and radiation therapy, but there are also treatments that target specific features of the lymphoma cells. If you have been diagnosed with lymphoma, you should consult your doctor and health website https://productossaludes.com/
to determine the best option for you. You may also have a biopsy to check for symptoms.
After consulting with your doctor, you can better assess your lymphoma risks. You can choose between chemotherapy and radiation therapy, or a combination of both. If you are concerned about your risk of developing lymphoma, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of each treatment. During treatment, you should see a specialist who has experience treating lymphoma.
There are several types of lymphoma. Some of them are asymptomatic, while others are resistant to treatment. A diagnosis is necessary to decide whether the cancer is treatable. In some cases, chemotherapy can help prolong a patient’s life. Your doctor will want to determine the type of cancer. Diagnosis and treatment will vary depending on the severity of the disease. If you suspect a person has lymphoma, your doctor may recommend certain treatments.
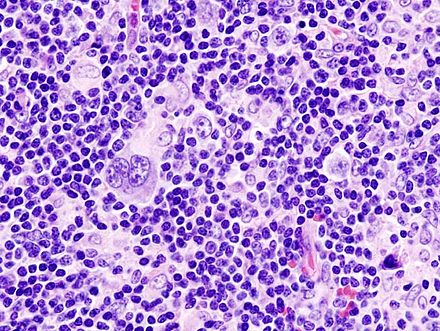
Cancer is caused by clonal proliferation of lymphocytes. There are two types of lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas are more common than Hodgkin’s lymphomas and are more common in children and adults. Both types of lymphoma are often curable. In fact, most patients survive this disease for many years. During treatment, the possibility of complications and other complications of the disease should be discussed.
The revised Euro-American classification of lymphomas uses genetic and immunophenotypic features to differentiate these entities. It includes a list of selected clinicopathological entities. For example, patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma may have a median survival of five years. It is usually a widespread condition that affects both men and women. It can also lead to gastrointestinal and pulmonary obstruction.
Depending on the type and grade of lymphoma, patients may experience remission for months or even years. While most patients experience a remission after lymphoma treatment, the length of the disease can vary. The longer the remission lasts, the higher the likelihood that the cancer will return. A remission can be a complete or partial remission, or a partial or complete remission. A partial remission is defined as the tumor shrinking less than half its original size. A full remission is defined as a disease where the tumor remains larger than half its original size.
